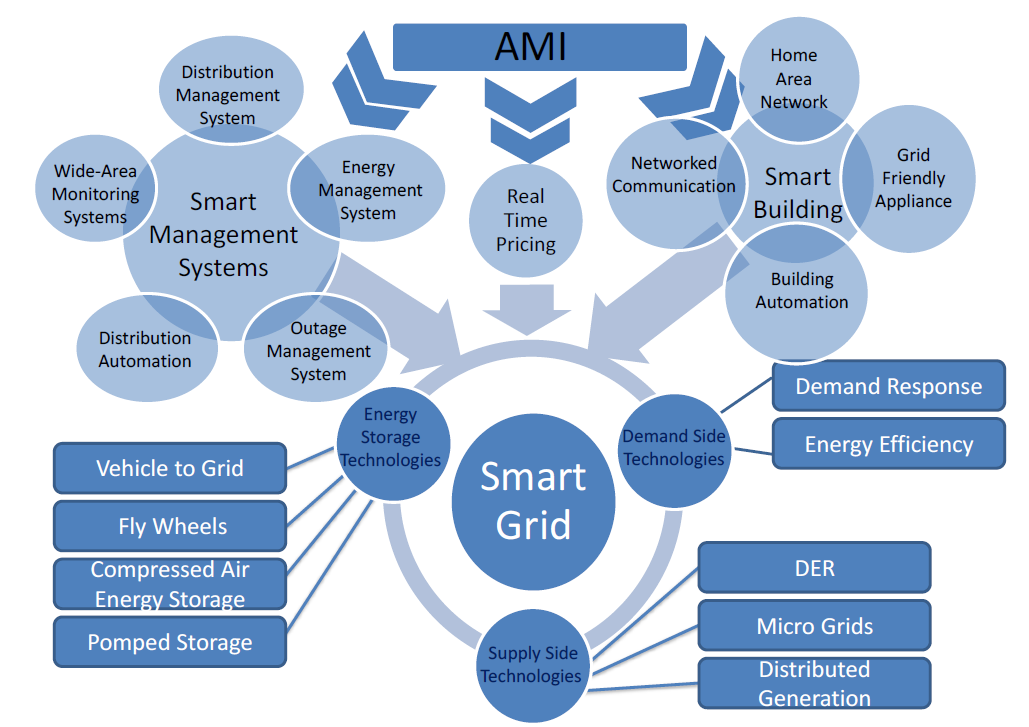
in short, smart grid is defined as many elements, all of which has a sameness in one subject, that is bilateral data flow corresponding to electricity energy current. As smart grid is involved in the all parts of the energy transformation cycle, from generation to consumption, the route of electricity current is converted from one-way case (generating electricity in the form of centralized and then transmit it through transmission and distribution networks to the final consumer) to two-way mode (figures 1 and 2). Also power system operation method is changed from hierarchical case (from up to bottom) to distributed control system. One of the main points about the smart grids is the increment in the observability and controllability rate of all of the processes in the grid. It is because the data is shared between different components and subsystems in the grid. Therefore standardizing the aforementioned total process is very vital, since the prerequisite of smart grid is to interact and percept the data reciprocally between all the equipments and devices, systems, software and hardware located in the entire electricity network. In this paper, it is tried to analyze the proposed standards in this field and cite the advantages and disadvantages of them and the route to their evolution.